Internet user safety has become a priority for the Google search engine. More about Google’s views on the security and protection of user data in this material. Online data theft has become a major problem and Google has taken action and reported that as of July 1, 2018, all website owners must have an SSL certificate. A statistic shows that in 2017 over 1500 people were victims of identity theft and suffered. As a complem ent we also recall the policy on personal data protection (GDPR) of EU citizens, which became mandatory on May 25, 2018.
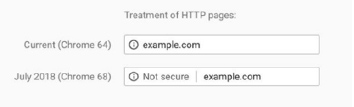
What is HTTPS?
Let’s start with the basics. S at the end of the “HTTP” part of a URL means that the site is secure. HTTPS (Security Hypertext Transport Security) sites mean tha t they are SSL certified and allow secure connections from a web server to a browser.
Secure sites can protect a user’s connection by securi ng information in three ways:
- encryption ensures that a user’s activ ity cannot be tracked and information cannot be stolen either
- data integrity prevents damage to files when they are transferred
- authentication protects against attacks and gives users confidence.
What is an SSL certificate?
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a data file that functions as a lock for a website. In essence, having an SSL certificate virtually eliminates the possibility of a hacker stealing personal data from a site. Websites that contain an SSL certificate have the HTTPS tag instead of the basic HTTP extension. By obtaining an SSL certific ate websites can additionally receive encryption to deter illegal data theft while users are browsing that website.
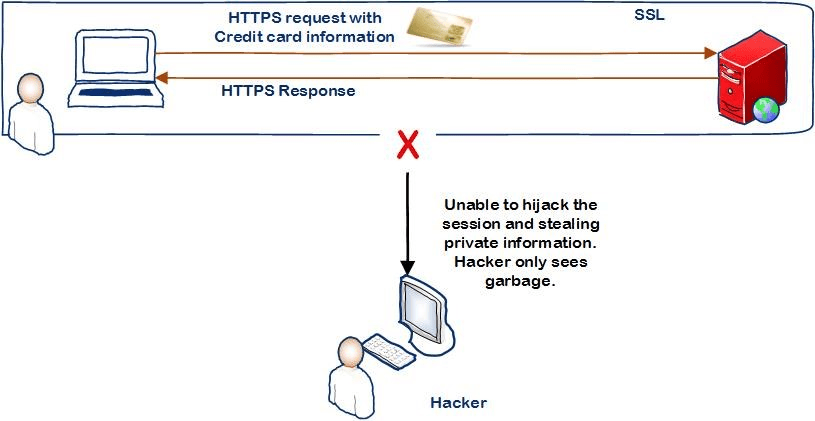
Many sites are unsafe and become easy prey for hackers. According to Wired, 79% of the 100 Google sites do not have high-quality web security. Google is trying to prioriti ze internet security by requesting the implementation of an SSL certificate. So, ignoring this, your site will suffer over time and it is possible to see this in the short term, especially since Google is constantly working on user safety.
Types of SSL certificates
Certificate with extended validation a – EV – offers the highest degree of security, trust, and conversion for website customers. It is issued only after a rigorous verification of the company. For this reason, the EV certificate contains a unique differentiator that clearly communicates the credibility of the site.
Company Validation Certificate – OV – includes full validation of companies from a certification authority. Each OV certificate contains the full name of the company, details about the address.
Certificate with domain validation -DV – offers the same high degree of data encryption, but does not offer guarantees regarding the identity of the business behind the site. If EV and OV certificates are issued only after the requesting organization has been manually verified by a certification authority, DV certificates are issued after domain control. DV certificates are the most popular due to their low price and short acceptance time.
The benefits of an SSL certificate
- An SSL certificate is an effective way to prevent data theft from your customers
- the presence of an SSL certificate presents security to users and trust in your site and brand, especially if we are talking about sites that ask customers for card data or personal information.
How to purchase an SSL certificate?
First of all, we must mention that most SSL certificates are FREE. There are also paid options, these being indicated for sites that manage a large volume of data from customers.
You can purchase the SSL certificate from your hosting provider. There are several companies that provide SSL certificates, such as Godaddy, Comodo, Namecheap, DigiCert and you should receive additional encryption at a reasonable price.
After you have installed the SSL certificate and made the configurations on your site, Chrome and Firefox will signal this. Your customers will be notified that they are on a safe site or not. If users are warned that they have reached an unsafe site, they will leave the site and will not complete the order or will stop browsing in the future for fear that their data is unsafe.

Some tips before you start implementing the certificate
- Decide what type suits you: single certificate, multi-domain, or wildcard.
- Use 2048-bit key certificate
- Use the appropriate URLs for resources that are on the same secure domain
- Do not block the HTTPS site from crawling using robots.txt
- Allow search engines to index pages where appropriate. Avoid the meta-tag of noindex robots.
- If the site is already running HTTPS you can check the security level using Qualys Lab.
Validity of the SSL certificate
The SSL certificate expires after 1 year from the purchase, so the annual renewal is necessary. Setting it up means a cost.
Common mistakes that can occur during the installation of the SSL certificate
- There are sites that have the HTTPS version, but they also have HTTP pages and have collected private information. Attention, any page that collects passwords must be encrypted.
- You have mixed content because there are images, links, scripts that have not been secured.
- The domain in the SSL certificate may be incorrect and then users do not have access to that page.
- Expired SSL certificate suggesting that users leave the page or access it with certain risks.
- It can happen that the internal links of the site lead from HTTPS to HTTP and then the search engines become confused about the version of the page they should classify.
- The detection of problems regarding possible errors in the installation of an SSL certificate can be done through an SEO audit even by Apptians.
How to transfer from HTTP to HTTPS without affecting your positions in Google?
- Install the SSL certificate. Make sure that you have bought a certificate of at least 2048 -bit. The certificate must be updated (an automatic renewal would be good) and a variant that works for www and non-www variants.
- Change the URL and make sure the site starts with HTTPS.
- Add 301 redirect and request redirection from HTTP to HTTPS. You installed the SSL certificate on the server, where you changed the URL. To gain SEO advantage, the site must be configured to redirect from HTTP to HTTPS. In other words, the URL for all your posts should start with HTTPS and not HTTP. The easiest way is to add the code below to the .htaccess file via FTP.
HTTPS redirect
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond% {HTTPS} off
RewriteCond% {HTTP_USER_AGENT}! FeedBurner [NC]
RewriteCond% {HTTP_USER_AGENT}! FeedValidator [NC]
RewriteRule (. *) Https: //% {HTTP_HOST} / $ 1 [R = 301, L]
After you have done this operation, open a window and do the check.
- Check and replace if you still have links that contain HTTP you need to replace them with HTTPS. Otherwise, the site will look unsafe. Before the operation, it would be good to make a backup of the site. If your site is built in WordPress, here you can use the search & replace plugin, which will make your work easier.
- Check the non-HTTPS external links.
- Check if you have links with problems!
- Add the HTTPS version in the google search console.
- Regenerate the XML sitemap and submit it to Google.
- Check Robots.txt. Make sure that the robots.txt file does not block search engine access from accessing the HTTPS site.
- Use Fetch as Google to verify that Google Bot is working properly.
- Update your Google Analytics profile from HTTP to HTTPS.
- Monitor your keyword search performance, but wait a few weeks.
The impact of HTTPS on SEO
- Google has been announcing since 2014 that a secure connection, HTTPS, is an important factor to consider for a good search engine placement.
- Although Google says that many indexing factors are equal, there are sites that have doubled their results, according to Google Analytics, after switching to HTTPS.
- If the HTTPS factor does not show a clear impact now, surely the results are on the way. Google will completely discourage searches on insecure sites, and those with HTTPS will have visibility in the SERP.
- Several studies have shown that there is a connection between HTTPS and better search engine positioning.
- The HTTPS site loads faster than HTTP, and this leads to a better rank.
- According to some stats, 84% of users give up when they see that the site is unsafe, which has an impact on sales. According to a survey, 84% of users would give up a purchase if their data were transmitted over an insecure connection.
- However, HTTPS migration is only one part of an SEO optimization that is influenced by factors such as page load speed, technical issues, page optimization.
- In the long run, it will be quite difficult to compete with secure sites and solve other problems that arise.
Conclusions
Data security has become a serio us issue and the HTTPS protocol is now mandatory. And from an SEO point of view, Google has clearly announced that the lack of an SSL certificate can lead to significant decreases in positions and inevitably to a decrease in traffic. Studies clearly show that a site with an SSL certificate has a better position on google. Even a recent experiment by MOZ shows that such a site has a higher chance of a position on the first page of the search engine.
Installing SSL is neither complicated nor costly. We have seen that most certificates are offered for free by hosting companies.
On the other hand, Google encourages the SSL certific ate not only for SEO reasons but also for an excellent user experience. The icon that confirms that the site you are browsing is safe, helps maintain your online reputation.
The SSL certificate is also secure for users who use unencrypted WI-FI from public places, we are talking about cafes, airports and other locations where they access the site. At the same time, the HTTPS version confirms to the user that it is connected to an authentic site and not a fake one.
Our tip: if you don’t have the SSL certificate installed yet, implement it right now!

Comments are closed.